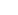EXTERNAL TRANSISTOR
It is recommended to design for V+ equal or greater than
7.5V with loop currents up to 30mA to allow for out-of-range
input conditions.
Transistor Q1 conducts the majority of the signal-dependent
4-20mA loop current. Using an external transistor isolates
the majority of the power dissipation from the precision input
and reference circuitry of the XTR105, maintaining excellent
accuracy.
The low operating voltage (7.5V) of the XTR105 allows
operation directly from personal computer power supplies
(12V ±5%). When used with the RCV420 current loop re-
ceiver (see Figure 7), the load resistor voltage drop is limited
to 3V.
Since the external transistor is inside a feedback loop, its
characteristics are not critical. Requirements are: VCEO = 45V
min, β = 40 min, and PD = 800mW. Power dissipation
requirements may be lower if the loop power-supply voltage
is less than 36V. Some possible choices for Q1 are listed in
Figure 1.
ADJUSTING INITIAL ERRORS
Many applications require adjustment of initial errors. Input
offset and reference current mismatch errors can be cor-
rected by adjustment of the zero resistor, RZ. Adjusting the
gain-setting resistor, RG, corrects any errors associated with
gain.
The XTR105 can be operated without this external transis-
tor, however, accuracy will be somewhat degraded due to
the internal power dissipation. Operation without Q1 is not
recommended for extended temperature ranges. A resistor
(R = 3.3kΩ) connected between the IRET pin and the E
(emitter) pin may be needed for operation below 0°C with-
out Q1 to ensure the full 20mA full-scale output, especially
with V+ near 7.5V.
2- AND 3-WIRE RTD CONNECTIONS
In Figure 1, the RTD can be located remotely simply by
extending the two connections to the RTD. With this remote
2-wire connection to the RTD, line resistance will introduce
error. This error can be partially corrected by adjusting the
values of RZ, RG, and RLIN1
.
A better method for remotely located RTDs is the 3-wire RTD
connection (see Figure 3). This circuit offers improved accu-
racy. RZ’s current is routed through a third wire to the RTD.
Assuming line resistance is equal in RTD lines 1 and 2, this
produces a small common-mode voltage that is rejected by
the XTR105. A second resistor, RLIN2, is required for linear-
ization.
10
V+
8
E
XTR105
0.01µF
Note that although the 2-wire and 3-wire RTD connection
circuits are very similar, the gain-setting resistor, RG, has
slightly different equations:
IO
7
2R1(R2 +RZ) – 4(R2RZ)
IRET
6
RG
=
2-wire:
3-wire:
R2 –R1
For operation without an external
transistor, connect a 3.3kΩ
resistor between pin 6 and pin 8.
See text for discussion
of performance.
2(R2 –RZ)(R1 –RZ)
R2 –R1
RG
=
R
Q = 3.3kΩ
where: RZ = RTD resistance at TMIN
R1 = RTD resistance at (TMIN + TMAX)/2
R2 = RTD resistance at TMAX
FIGURE 2. Operation Without an External Transistor.
To maintain good accuracy, at least 1% (or better) resistors
should be used for RG. Table I provides standard 1% RG
resistor values for a 3-wire Pt100 RTD connection with
linearization.
LOOP POWER SUPPLY
The voltage applied to the XTR105, V+, is measured with
respect to the IO connection, pin 7. V+ can range from 7.5V
to 36V. The loop-supply voltage, VPS, will differ from the
voltage applied to the XTR105 according to the voltage drop
on the current sensing resistor, RL (plus any other voltage
drop in the line).
LINEARIZATION
RTD temperature sensors are inherently (but predictably)
nonlinear. With the addition of one or two external resistors,
If a low loop-supply voltage is used, RL (including the loop
wiring resistance) must be made a relatively low value to
assure that V+ remains 7.5V or greater for the maximum loop
current of 20mA:
RLIN1 and RLIN2, it is possible to compensate for most of this
nonlinearity resulting in 40:1 improvement in linearity over
the uncompensated output.
See Figure 1 for a typical 2-wire RTD application with
linearization. Resistor RLIN1 provides positive feedback and
controls linearity correction. RLIN1 is chosen according to the
desired temperature range. An equation is given in Figure 1.
(V+) – 7.5V
RL max =
–RWIRING
20mA
XTR105
SBOS061B
9
www.ti.com