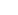NX2114/2114A
dependent.
Power MOSFETs Selection
The NX2114 requires two N-Channel power
MOSFETs. The selection of MOSFETs is based on
maximum drain source voltage, gate source voltage,
maximum current rating, MOSFET on resistance and
power dissipation. The main consideration is the power
loss contribution of MOSFETs to the overall converter
efficiency. In this design example, two Fairchild FDS6294
are used. They have the following parameters: VDS=30V,
ID =13A, RDSON =14.4mW,QGATE =10nC.
Soft Start, Enable and shut Down
The NX2114 has a digital start up. It is based on
digital counter with 1024 cycles. For NX2114 with 300kHz
operation, the start up time is about 3.5ms. For NX2114A
with 600kHz operation, the start up time is about half of
NX2114, 1.75mS.
NX2114/NX2114A can be enabled or disabled by
pulling COMP pin below 0.3V. The function is illustrated
in the following diagram. During the normal operation,
the lowest COMP voltage is clamped to be about 700mV
, the COMP voltage is higher than 0.3V. If external switch
with 10W Rdson or less to pull down COMP pin, when
COMP is below 0.3V, the digital soft start will be reset to
zero. All the drivers will be off. The synchronous buck is
shut off. When external switch is released, and COMP
is above 0.3V, a soft start will initiates and system starts
from the beginning.
There are three factors causing the MOSFET power
loss: conduction loss, switching loss and gate driver loss.
Gate driver loss is the loss generated by discharg-
ing the gate capacitor and is dissipated in driver circuits.
It is proportional to frequency and is defined as:
...(20)
Pgate = (QHGATE ´ VHGS + QLGATE ´ VLGS )´ FS
where QHGATE is the high side MOSFETs gate
charge, QLGATE is the low side MOSFETs gate charge,
VHGS is the high side gate source voltage, and VLGS is
the low side gate source voltage.
According to equation (20), PGATE =0.03W. This
power dissipation should not exceed maximum power
dissipation of the driver device.
Conduction loss is simply defined as:
2114
Shut
down
2
PH C O N =IO U T ´ D ´ R D S ( O N ) ´ K
FB
2
PL C O N =IO U T ´ (1 - D ) ´ R D S (O N ) ´ K
Compensation
Network
PT O T A L =PH C O N + PL C O N
...(21)
0.3V
where the RDS(ON) will increases as MOSFET junc-
tion temperature increases, K is RDS(ON) temperature
dependency. As a result, RDS(ON) should be selected for
the worst case, in which K equals to 1.43 at 125oC
according to FDS6294 datasheet. Using equation (21),
the result of PTOTAL is 0.75W. Conduction loss should
not exceed package rating or overall system thermal
budget.
comp
0.6
OFF
ON
1.3V
Clamp
Figure 14 - Enable and Shut down NX2114 by
pulling down COMP pin.
Switching loss is mainly caused by crossover con-
duction at the switching transition. The total switching
Feedback Under Voltage Shut Down
NX2114 relies on the Feedback Under Voltage Lock
Out (FB UVLO ) to provide short circuit protection. Ba-
sically, NX2114 has a comparator compare the feedback
voltage with the FB UVLO threshold 0.4V.
loss can be approximated.
1
PSW
=
´ VIN ´ IOUT ´ TSW ´ FS
...(22)
2
where IOUT is output current, TSW is swithing time,and FS
is switching frequency. Swithing loss PSW is frequency
Rev. 4.0
06/20/06
14