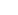NX2113/2113A
There are three factors causing the MOSFET power
loss: conduction loss, switching loss and gate driver loss.
Gate driver loss is the loss generated by discharg-
ing the gate capacitor and is dissipated in driver circuits.
It is proportional to frequency and is defined as:
Vbus
POR
R1
R2
Digital
start
up
OFF
10k
EN
1.25/1.15
ON
Pgate = (QHGATE ´ VHGS + QLGATE ´ VLGS )´ FS
...(20)
where QHGATE is the high side MOSFETs gate
charge,QLGATE is the low side MOSFETs gate charge,VHGS
is the high side gate source voltage, and VLGS is
the low side gate source voltage.
Figure 14 - Enable and Shut down NX2113 by
pulling down EN pin.
According to equation (20), PGATE =0.14W. This
power dissipation should not exceed maximum power
dissipation of the driver device.
The start up of NX2113/2113A can be programmed
through resistor divider at Enable pin. For example, if
the input bus voltage is 12V and we want NX2113 starts
when Vbus is above 8V. We can select
R2=1.24k
Conduction loss is simply defined as:
P
HCON =IOUT2 ´ D´ RDS(ON) ´ K
LCON=IOUT2 ´ (1- D)´ RDS(ON) ´ K
PTOTAL =P + P
P
...(21)
(8V - 1.25V)´ R2
HCON
LCON
R1 =
= 6.8kW
1.25V
where the RDS(ON) will increases as MOSFET junc-
tion temperature increases, K is RDS(ON) temperature
dependency. As a result, RDS(ON) should be selected for
the worst case, in which K equals to 1.4 at 125oC ac-
cording to IRFR3706 datasheet. Using equation (21),
the result of PTOTAL is 0.54W. Conduction loss should
not exceed package rating or overall system thermal
budget.
The NX2113 can be turned off by pulling down the
ENable pin by extra signal MOSFET or NPN transistor
such as 2N3904 as shown in the above Figure. When
Enable pin is below 1.15V, the digital soft start is reset
to zero. In addition, all the high side is off and output
voltage is turned off.
A resistor should be added as preload to prevent
leakage current from FB pin charging the output capaci-
tors.
Switching loss is mainly caused by crossover con-
duction at the switching transition. The total switching
loss can be approximated.
Feedback Under Voltage Shut Down
NX2113 relies on the Feedback Under Voltage Lock
Out (FB UVLO ) to provide short circuit protection. Ba-
sically, NX2113 has a comparator compares the feed-
back voltage with the FB UVLO threshold 0.4V.
During the normal operation, if the output is short,
the feedback voltage will be lower than 0.4V and com-
parator will change the state.After certain internal delay,
both high side and low side driver will be turned off. The
output will be latched. The normal operation should be
achieved by removing the short and recycle the VCC.
During the start up, the output voltage is dis-
1
PSW
=
´ V ´ IOUT ´ TSW ´ F
IN S
...(22)
2
where IOUT is output current, TSW is the sum of TR and TF
which can be found in mosfet datasheet, and FS is switch-
ing frequency. The result of PSW is 3W. Swithing loss
PSW is frequency dependent.
Soft Start, Enable and shut Down
The NX2113 has a digital start up. It is based on
digital counter with 1024 cycles. For NX2113 with 300kHz
operation, the start up time is about 3.5ms. For NX2113A
with 600kHz operation, the start up time is about half of
NX2113, 1.75mS.
charged to zero by the synchronous FET. FB voltage
starts increase from zero when digital start block
Rev. 2.0
11/18/05
15