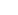NX2116/2116A/2116B/2117/2117A
sired voltage decided by the feedback resistor divider.
P
HCON =IOUT2 ´ D´ RDS(ON) ´ K
LCON=IOUT2 ´ (1- D)´ RDS(ON) ´ K
PTOTAL =P + P
P
...(20)
Vbus
HCON
LCON
where the RDS(ON) will increases as MOSFET junc-
tion temperature increases, K is RDS(ON) temperature
dependency. As a result, RDS(ON) should be selected for
the worst case, in which K approximately equals to 1.4
at 125oC according to IRFR3709Z datasheet. Conduc-
tion loss should not exceed package rating or overall
system thermal budget.
POR
R1
R2
Digital
start
up
OFF
10k
EN
ON
1.25V/
1.15V
Figure 9 - Enable and Shut down the NX2116
with Enable pin.
Switching loss is mainly caused by crossover con-
duction at the switching transition. The total switching
loss can be approximated.
The start up of NX2116 can be programmed through
resistor divider at Enable pin. For example, if the input
bus voltage is12V and we want NX2116 starts when Vbus
is above 9V. We can select using the following equa-
tion.
1
PSW
=
´ V ´ IOUT ´ TSW ´ F
IN S
...(21)
2
where IOUT is output current, TSW is the sum of TR
and TF which can be found in mosfet datasheet, and FS
is switching frequency. Switching loss PSW is frequency
dependent.
(9V - 1.25V)´ R2
R1 =
1.25V
The NX2116 can be turned off by pulling down the
Enable pin by extra signal MOSFET as shown in the
above Figure. When Enable pin is below 1.25V, the digi-
tal soft start is reset to zero. In addition, all the high side
and low side driver is off and no negative spike will be
generated during the turn off.
Also MOSFET gate driver loss should be consid-
ered when choosing the proper power MOSFET.
MOSFET gate driver loss is the loss generated by dis-
charging the gate capacitor and is dissipated in driver
circuits.It is proportional to frequency and is defined as:
P
= (QHGATE ´ VHGS + QLGATE ´ VLGS )´ FS
...(22)
gate
where QHGATE is the high side MOSFETs gate
Over Current Protection
charge,QLGATE is the low side MOSFETs gate charge,VHGS
is the high side gate source voltage, and VLGS is the low
Over current protection is achieved by sensing cur-
rent through the low side MOSFET. An internal current
source of 40uA flows through an external resistor con-
nected from OCP pin to SW node sets the over current
protection threshold. When synchronous FET is on, the
voltage at node SW is given as
side gate source voltage.
This power dissipation should not exceed maxi-
mum power dissipation of the driver device.
Soft Start and Enable
VSW =-IL ´ RDSON
NX2116 has digital soft start for switching control-
ler and has one enable pin for this start up. When the
Power Ready (POR) signal is high and the voltage at
enable pin is above 1.25V the internal digital counter
starts to operate and the voltage at positive input of Error
amplifier starts to increase, the feedback network will
force the output voltage follows the reference and starts
the output slowly. After 2048 cycles, the soft start is
complete and the output voltage is regulated to the de-
The voltage at pin OCP is given as
IOCP ´ ROCP +VSW
When the voltage is below zero, the over current
occurss as shown in figure 10.
Rev. 3.0
03/14/06
13